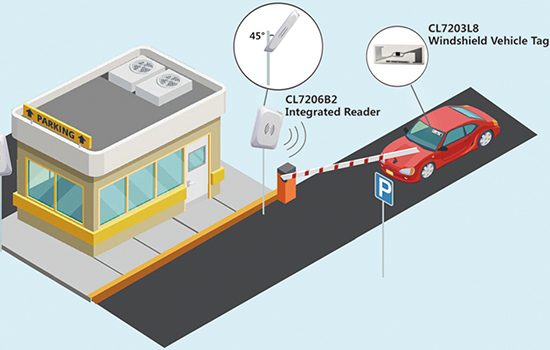
Radio-frequency identification (RFID) is a wireless technology that uses radio waves to identify digital data encoded in RFID tags with an RFID reader. An RFID system consists of two main components, i.e., the front end and the back end. The front end comprises embedded integrated circuit (IC) tags (RFID transponders) and readers (RFID transceivers), while the rear end comprises a database or server that manages the RFID data of the tag.
In this digitalized era, RFID technology has a lot of applications, such as supply chain management, inventory management, automated logistics, healthcare, agriculture, retail, and many more. In short, RFID has become a key component of IoT systems and applications. Despite the benefits, many are concerned about data security with RFID technology because RFID tags often store sensitive information, such as medical records, financial data, and others. So, let's explore the security concerns of RFID and the best way to minimize RFID security risks.
Security Concerns of RFID Technology
Since RFID technology can accurately capture data and enable real-time tracking and monitoring, it also triggers security threats. Below are the top three security concerns of RFID:
1) RFID Data Counterfeiting: Eavesdropping & Replay
RFID technology identifies the tag using electrostatic or electromagnetic coupling in the radio frequency portion of the electromagnetic spectrum. This means that the wireless transmission of the data increases the risk of data counterfeiting. Simply put, a third party can intercept or modify the data transmitted between the RFID tag and the RFID device.
Eavesdropping is one of the main RFID data counterfeiting threats in which the attacker uses the antenna to intercept the communication between the tag and the reader. Alternatively, attacks can conduct data counterfeiting by replay approach where the transmitting data is recorded and then replayed later to impersonate the original tag. In short, data counterfeiting can compromise RFID data security and even manipulate the data being used in financial transactions or access control.
2) Manual Attacks
Other than wireless interception, RFID technology is also vulnerable to manual attacks in which attackers interfere with the reader or tag physically. For example, they might clone an RFID tag or tamper with the reader's signal to break a secure facility. In addition, they can execute other manual attacks, such as altering/removing the tag to change identity, jamming the reader's signal, etc.
3) Denial of Service (DoS) Attacks
Attackers can also initiate denial of service (DoS) attacks in which they send a stream of requests to the RFID reader, eventually overwhelming it. This will lead to malfunction or damage to the RFID reader and make it unable to address legitimate requests. Such attacks lead to disruption of operations and downtimes.
Apart from the above three attacks, RFID data can be vulnerable to other emerging security threats. However, most of these security threats can be minimized significantly with the proper use of RFID technology and security measures.

Hopeland – Offering Secure RFID Products with the use of RAIN RFID Chips
Hopeland Technologies is a leading provider of high-tech RFID products. Known for specializing in the research and development of RFID technologies, Hopeland has responded to the surging demand for more secure RFID data technology using RAIN RFID chips in its products.
RAIN RFID is a type of ultra-high frequency (UHF) RFID technology that minimizes many RFID data security risks through its built-in protection mechanisms, as follows:
1) Passive Tags: RAIN RFID is passive, which means the tags won't emit any signal until the reader asks.
2) Data Killing Feature: RAIN RFID tags can be deactivated permanently so that they don't respond to other requests.
3) Authentication: RAIN RFID chips can be programmed with an authentication protocol so that the tag can remain silent until the reader inputs the pin.
4) Tamper Detection: RAIN RFID chips are programmable with tamper detection mechanisms, which can generate an alarm or signal if the tag is removed or altered.
5) Short-Range Mode: RAIN RFID tags can be switched to a short-range mode so that they only respond closely to the reader.
Hopeland RFID Readers for Recommendation
Overall, the Hopeland RFID products with RAIN RFID chips provide the performance and security that customers expect from RFID technology today. Here listed the examples:

Hopeland HT100 Industrial Integrated RFID Reader is powered by an Impinj RAIN RFID E510 chip and offers features like adjustable RF output power, automatic/command tag reading mode, support RSSI, and many more. It finds application in intelligent meter warehousing, fixed asset management, textile production, etc.

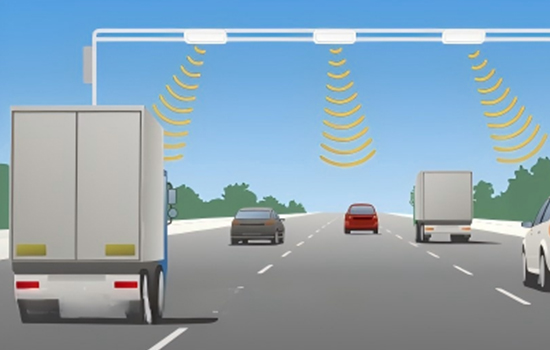
Similarly, Hopeland HF100 2-port Integrated RFID Reader is powered by an Impinj RAIN RFID E710 chip and offers more advanced features like reading up to 600-900 tags/second, temperature and humidity sensor, higher sensitivity -85dbm, support wireless communication (Bluetooth and Wi-Fi), etc. It finds application in highway RFID tolling, RFID parking access, innovative warehousing, etc.
Wrapping Up
RFID technology plays a significant role in today's business world for managing, tracking, and identifying objects and assets. On the same side, there are several RFID data security risks if the technology is not used rightly. However, Hopeland is strongly committed to addressing the issues with its RAIN RFID chips-based RFID devices. To sum up, ensure that the RFID device and technology you use adhere to the best security measures to protect your RFID data. Alternatively, avoid all the hassle by picking the reliable products of Hopeland.